
News
Good News | Maband Pharmaceutical Group's Mecobalamin Granted Orphan Drug Designation by the U.S. FDA for the Treatment of ALS
Date:
14 Apr,2025
Good News
Wanbande Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd.
Mecobalamin Approved by the U.S. FDA
Granting Orphan Drug Designation for ALS Treatment
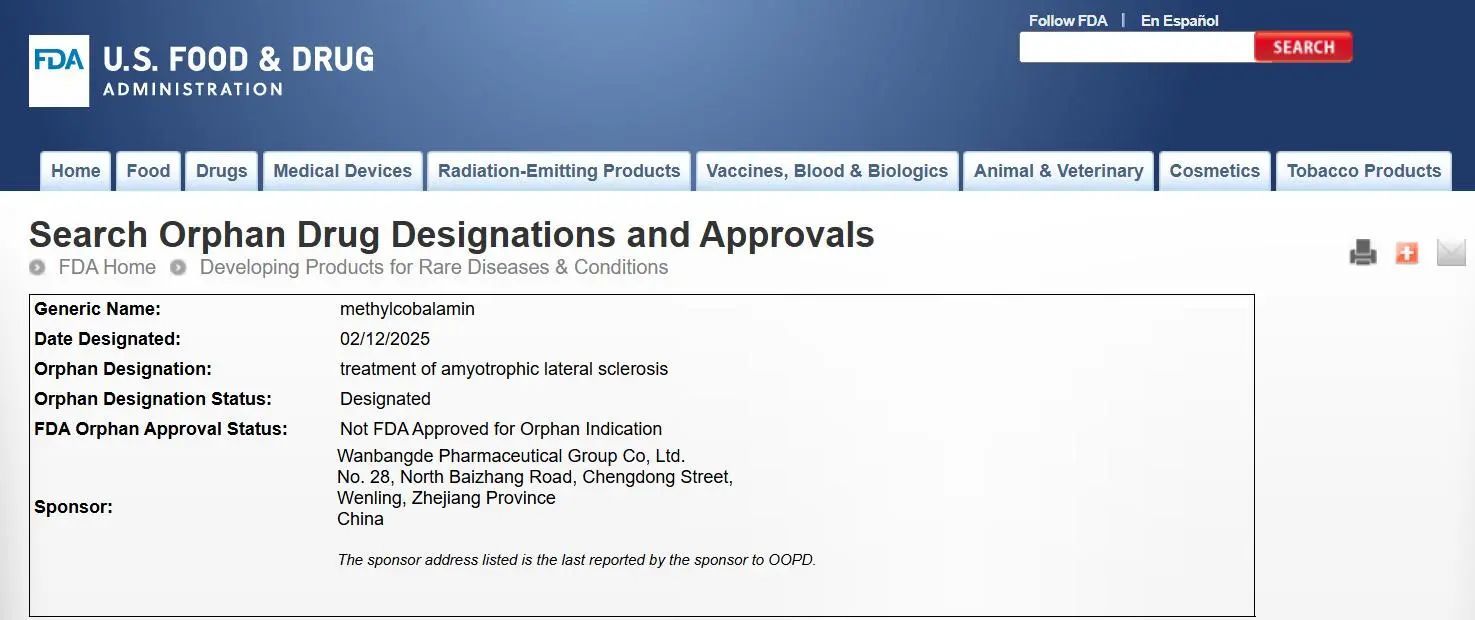
On February 14, 2025, Wanbangde Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. announced that its investigational new drug, methylcobalamin, has received Orphan Drug Designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease.
The orphan drug designation is a qualification established by the FDA to encourage the development of treatments for rare diseases, offering a range of incentives to support new drug development. These incentives include a 7-year period of market exclusivity starting from the approval of the drug, priority review and approval for New Drug Applications (NDAs), close guidance and support throughout clinical development, and waivers of NDA submission fees. In 2025, the U.S. FDA’s fee for a New Drug Application was $4,310,002 (approximately 31 million RMB).
“We are thrilled that mecobalamin has been granted Orphan Drug Designation by the U.S. FDA for the treatment of ALS,” said Dr. Zhao Guanjia, Head of R&D at Wanbangde Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. “Currently, we are actively advancing the global development of mecobalamin as a new therapeutic option, and we look forward to bringing this innovative treatment to more ALS patients around the world at the earliest possible opportunity.”
About Mecobalamin
Mecobalamin is a vitamin B12 analog and the only form of vitamin B12 that can cross the blood-brain barrier without requiring biological conversion. It efficiently circulates throughout the body and is stored in the liver, but it is primarily utilized by brain cells—especially neurons.
As a coenzyme of methionine synthase, methylcobalamin catalyzes the conversion of homocysteine into methionine, thereby maintaining the balance of the methylation cycle and reducing the neurotoxicity of homocysteine. Elevated homocysteine levels can lead to excessive activation of NMDA receptors, triggering calcium overload, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ultimately cell apoptosis—mechanisms closely linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS. Clinical evidence indicates that ALS patients exhibit significantly higher levels of homocysteine in their cerebrospinal fluid. Methylcobalamin helps mitigate homocysteine accumulation through metabolic regulation, while also directly protecting neurons from glutamate-induced toxicity. Moreover, in animal models, it has been shown to promote nerve regeneration and repair, improving nerve conduction in conditions like sciatic nerve injury and diabetic neuropathy. These findings underscore methylcobalamin’s dual neuroprotective mechanisms and highlight its promising potential for treating neurodegenerative disorders.
The FDA's recent Orphan Drug Designation provides strong support and assurance for the company’s drug development efforts in the ALS field, as well as its global expansion strategy.
Notably, Eisai's methycobalamin lyophilized powder for injection received approval in Japan in September 2024 for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Eisai holds orphan drug designation for methycobalamin in Japan for ALS treatment, granting the company a 10-year exclusive marketing right in the Japanese market.
About ALS
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), commonly known as "Lou Gehrig's disease," is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, typically striking middle-aged and older adults between the ages of 40 and 70.[7] Motor neurons play a critical role in controlling the body's voluntary muscle movements; as these neurons gradually die off, muscles lose their nerve-driven control, leading to weakness, atrophy, and eventually paralysis.
Early symptoms of ALS typically include localized muscle weakness or atrophy, such as decreased grip strength in the hands, difficulty walking, or facial stiffness—symptoms that gradually spread throughout the body, leading to muscle spasms, slurred speech, and trouble swallowing. In advanced stages, patients may even become dependent on mechanical ventilation due to weakening of the respiratory muscles. Some individuals also experience mood swings or cognitive decline, which are often linked to damage in the brain’s frontal and temporal lobes. Once diagnosed, most patients survive only 2 to 3 years, with respiratory failure ultimately becoming the primary cause of death.
The pathogenesis of ALS is complex, involving interactions among genetic, molecular, and environmental factors. Approximately 90% of cases are sporadic, with no direct genetic link, while in the remaining 10% of familial cases, mutations in the C9orf72 and SOD1 genes are the most common genetic triggers.[6,7] Although sporadic cases lack clear genetic mutations, environmental factors such as exposure to heavy metals, smoking, or engaging in high-intensity exercise may accelerate neuronal death by triggering oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Globally, the incidence of ALS is about 1.68 cases per 100,000 person-years, but in the U.S., it rises significantly to 4.4 cases per 100,000 people. With the global population aging, the prevalence of ALS is expected to continue increasing in the years ahead.
Currently, there is no cure for ALS; treatment primarily focuses on slowing disease progression and improving quality of life. The drug riluzole helps extend patients' survival by inhibiting glutamate release, adding about 3 months to their lifespan. Meanwhile, the antioxidant edaravone can help slow down the decline of neurological function. In 2023, the gene-targeted therapy Tofersen was approved specifically for patients with SOD1 mutations, blocking the production of toxic proteins. Additionally, a combination therapy using dextromethorphan and quinidine has shown promise in alleviating symptoms of emotional instability. Supportive treatments such as non-invasive ventilators, nutritional management, and rehabilitation exercises are crucial for enhancing patients' daily lives. However, therapies like stem cell therapy and gene-editing techniques remain in the exploratory phase. Unfortunately, existing medications often suffer from unclear mechanisms, significant side effects, or high costs, leaving most patients still grappling with the harsh reality of having "no effective treatment options."
About Wanbande Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd.
Founded in 1970 and headquartered in Wenling City, Taizhou, Zhejiang Province, Wanbangde Pharmaceutical Group is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research, development, manufacturing, and sales of modern Chinese medicines, chemical APIs, and pharmaceutical preparations. With a registered capital of 360 million yuan, the company currently operates six subsidiaries and holds 185 approved drug production licenses covering 14 dosage forms. Wanbangde has consistently earned recognition as one of "China's Top 50 Fastest-Growing Companies in the Pharmaceutical Industry," a "Top 100 Brand Enterprise in Traditional Chinese Medicine," "China's Most Promising Pharmaceutical Company," and one of "China's Top 100 Manufacturers of Traditional Chinese Medicines." Additionally, the company's registered trademark has been officially recognized as a China Well-Known Trademark.
Guided by the pharmaceutical R&D philosophy of "patient-centric, globally oriented, and future-focused," the company is not only committed to enhancing the market competitiveness of its generic drug formulations and active pharmaceutical ingredients through differentiated development but also plans to strategically advance the development of Class 1 new drugs (new chemical entities) as well as Class 2 new drugs leveraging the 505(b)(2) pathway. Additionally, Wanbangde Pharmaceutical Group is actively pursuing global partnerships to accelerate drug innovation and expand into overseas markets, ultimately benefiting a broader patient population. This comprehensive strategy aims to deliver safer, more effective clinical treatment options, addressing the growing demands of patients worldwide.

Related Recommendations
